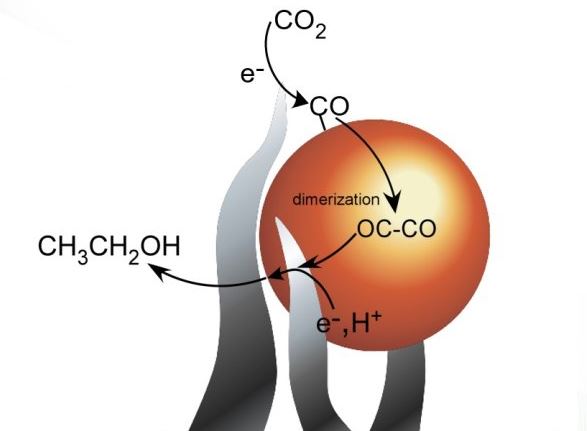
A team of researchers has made significant strides in the efficient conversion of carbon dioxide (CO2) into ethanol, utilizing copper nanocubes coated with zinc oxide. This novel approach enhances the catalytic process, shielding the copper catalyst and optimizing reaction conditions, leading to a marked reduction in by-products such as hydrogen.
The breakthrough relies on pulsed electrochemical CO2 reduction, combined with zinc oxide, to improve ethanol yield while ensuring the long-term stability of the catalyst.
This advancement presents a sustainable and cost-effective method for ethanol production, furthering efforts to create green energy alternatives.
The research holds promise for addressing global carbon emissions by transforming CO2, a major greenhouse gas, into a valuable fuel source. By improving the efficiency of the conversion process, this innovation could potentially lower the cost of ethanol production, making it more viable for widespread industrial use.
Experts suggest that this method could be integrated into existing carbon capture systems, offering a dual benefit of reducing atmospheric CO2 levels while producing renewable energy. As the world moves towards cleaner energy solutions, this breakthrough represents a crucial step in the ongoing battle against climate change.
Key Points
- Breakthrough in CO2-to-Ethanol Conversion: Scientists developed a more efficient method using copper nanocubes coated with zinc oxide.
- Enhanced Catalyst Protection: Zinc oxide coating optimizes reaction conditions and shields the copper catalyst, reducing unwanted by-products like hydrogen.
- Sustainable and Cost-Effective: The new process improves ethanol production efficiency, making it a more affordable green energy solution.
- Pulsed Electrochemical Technique: The use of pulsed electrochemical CO2 reduction significantly boosts ethanol yield while maintaining catalyst stability.
- Impact on Carbon Capture: This method could be integrated with existing systems to both reduce CO2 emissions and produce renewable energy, aiding in climate change mitigation.