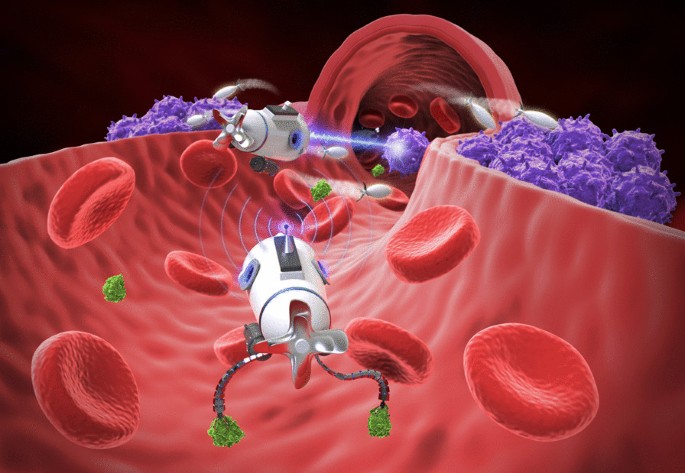
In a groundbreaking development, researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have unveiled a pioneering microbot made from seaweed that could revolutionize cancer treatment. These microbots, the first of their kind, possess the remarkable ability to navigate within cellular networks and target individual cells with precision.
Led by Berna Ozkale Edelmann, the team at TUM envisions a future where these microbots usher in new treatment methods for cancer patients and those grappling with other diseases. Ozkale Edelmann emphasized the potential of this innovation, stating, “We are using these microrobots to build tissues under synthetic conditions. And the whole point of this is to then – in the future – repair damaged tissue or organs based on the patient.”
Also Read: U.S. Agencies Aware of Wuhan Virus Creation in 2018, Newly Revealed Documents
Measuring just half the width of a human hair, these tiny robots are comparable in size to human cells. They boast a soft, flexible structure akin to human cells, enabling wireless control for precise manoeuvring within biological environments.
Philipp Harder, a PhD student involved in the project, elaborated on the technology’s capabilities, revealing, “We have gold nanoparticles inside the robots. And with a laser, which we can see here, we can heat certain areas of the robot… we can then move it within the cell clusters and move it to other locations and then look at several cells in different ways.”
Despite the promise these microbots hold, Ozkale Edelmann cautioned that they are not yet ready for direct application in cancer treatment. However, they are already proving invaluable in advancing ongoing research efforts. She emphasized the importance of further understanding cellular mechanisms to refine therapeutic approaches.
As this groundbreaking research continues to unfold, the potential for seaweed-based microbots to revolutionize cancer treatment grows ever more tangible. With their ability to navigate cellular landscapes and stimulate individual cells, these tiny robots represent a beacon of hope in the fight against cancer and other diseases.
Key Points:
- Innovative Microbots: Researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have developed microbots made from seaweed, a pioneering advancement in medical technology.
- Precision Targeting: These microbots possess the unique capability to navigate within cellular networks and stimulate individual cells with precision, offering a potential breakthrough in cancer treatment and other diseases.
- Size and Structure: Measuring only half the width of a human hair, these tiny robots are comparable in size to human cells. Their soft, flexible structure enables wireless control for precise manoeuvring within biological environments.
- Gold Nanoparticles and Laser Control: The microbots contain gold nanoparticles, allowing researchers to control their movement using a laser. This technology enables precise manipulation within cell clusters, facilitating detailed cellular analysis.
- Ongoing Research: While not yet ready for direct application in cancer treatment, these microbots are already contributing to significant advancements in research. Further understanding of cellular mechanisms is crucial for refining therapeutic approaches.
- Future Implications: As research progresses, the potential for seaweed-based microbots to revolutionize cancer treatment becomes increasingly promising. Their ability to navigate cellular landscapes and stimulate individual cells represents a beacon of hope in the fight against cancer and other diseases.